Documents show hepatitis B vaccine is not proven safer than hepatitis B for normal-risk children
NEWPORT BEACH, Calif., September 13, 2022 (Newswire.com) – Physicians for Informed Consent (PIC) has released two new educational documents: Hepatitis B – Disease Information Statement (DIS) “Hepatitis B: What Parents Need to Know” and Hepatitis B – Vaccine Risk Statement (VRS) “Hepatitis B Vaccine: Is It Safer Than Hepatitis B?” Developed from data compiled by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Center for Health Statistics, the documents assist readers in assessing the risks of hepatitis B compared to the risks of the hepatitis B vaccine, so they can engage in making an informed vaccine decision.
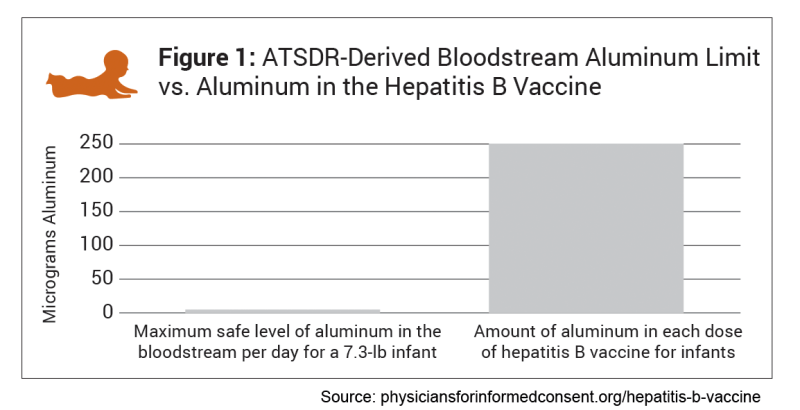
“New parents need to know that if their infants are normal-risk, which 99% of newborns are, then the chance of them getting fatal hepatitis B is 0.00001% or one in seven million — a prevaccine statistic,” said PIC founder and President Dr. Shira Miller. “They also need to know that all hepatitis B vaccines include the neurotoxin aluminum — which means there’s a 100% guarantee their infant will be exposed to aluminum if they get injected with a hepatitis B vaccine. And finally, they need to know that for newborns specifically, because of their low body weight, it appears that the amount of aluminum in hepatitis B vaccines exceeds the maximum safety levels established by the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, a division of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.”
Packed with relevant scientific information, the documents answer numerous important questions, including:
- What is hepatitis B?
- What are side effects of the hepatitis B vaccine?
- Is the hepatitis B vaccine safer than hepatitis B?
The documents present key facts and figures that are essential for informed decision-making. For example:
- An unvaccinated normal-risk child has a 1 in 7,000,000 (or 0.00001%) chance of contracting fatal hepatitis B annually.
- About 50% of hepatitis B-vaccinated children lose their immunity by age 5, and the vaccine has not made a measurable impact on the prevalence of chronic hepatitis B infection.
- Seizures may occur in about 1 in 1,300 children vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
- The hepatitis B vaccine contains an amount of aluminum that’s 75 times greater than the maximum safe level of aluminum in the bloodstream per day for a 7.3-pound infant.
- The Institute of Medicine (IOM) found that evidence is inadequate to rule out the possibility that hepatitis B vaccination leads to more than two dozen neurological and autoimmune disorders.
The Physicians for Informed Consent documents demonstrate that the hepatitis B vaccine is not proven to be safer than hepatitis B for normal-risk children. Parents and healthcare providers are encouraged to read these new documents to make an informed risk-benefit calculation.
To read the documents, visit physiciansforinformedconsent.org/hepatitis-b.
Press Contact:
info@picphysicians.org
925-642-6651
###
CLICK HERE to view on Newswire
CLICK HERE to view on Instagram
CLICK HERE to view on Facebook
CLICK HERE to view on Twitter
CLICK HERE to view on LinkedIn